Inverter Heat Sink Overview
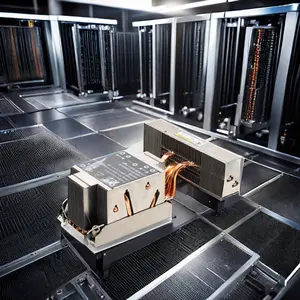
An inverter heat sink is a critical component in managing the thermal performance of power electronics. Serving as a thermal conductor, a heat sink facilitates heat transfer from the high-temperature device to the cooler environment. Inverters, being the heart of power conversion processes, generate significant amounts of heat and require efficient thermal management systems to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Types and Materials
Heat sinks for inverters come in various types, including stamped, extruded, bonded/fabricated, and cast. The choice of type often depends on the thermal requirements and the specific application of the inverter. Materials play a pivotal role in the effectiveness of a heat sink, with aluminum and copper being the most prevalent due to their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight characteristics.
Design and Features
The design of an inverter heat sink is tailored to maximize surface area in contact with the cooling medium, such as air or coolant. Features like fins and pin arrays are incorporated to increase the surface area, thus enhancing the heat dissipation rate. Advanced designs may also include heat pipes or vapor chambers for more demanding thermal management needs.
Applications and Advantages
Inverter heat sinks are utilized in a range of applications from solar inverters to electric vehicle power systems. The advantages of using a robust heat sink include improved inverter efficiency, reduced risk of overheating, and extended device lifespan. The passive cooling mechanism of a heat sink is also advantageous for its reliability and maintenance-free operation.
Thermal Performance and Selection
Selecting the right inverter heat sink involves understanding the thermal resistance and the environment in which the inverter operates. Factors such as ambient temperature, airflow, and mounting orientation all influence the thermal performance of a heat sink. A well-chosen heat sink will ensure that the inverter operates within its safe temperature range, even under full load conditions.
Environmental Considerations
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, the environmental impact of manufacturing and recycling heat sinks is also a consideration. Materials like aluminum are favored for their recyclability, contributing to the eco-friendly aspect of inverter heat sinks.
































 浙公网安备 33010002000092号
浙公网安备 33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4